When more is too much in cybersecurity
Discover How You Can Slash Cyberattack Risk by Over 85%
In the fast-paced world of cybersecurity, organizations are constantly striving to protect their digital assets from an ever-growing array of threats. However, there is a fine line between comprehensive security and overcomplication. With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, organizations must prioritize cybersecurity measures to protect their sensitive data, infrastructure, and reputation.
With numerous threats and limited resources, this can be difficult. The challenge lies in identifying the controls that will have the most significant impact on an organization’s security posture. When organizations adopt numerous security tools without a clear strategy, they can inadvertently create an overcomplicated cybersecurity environment. This complexity can lead to a range of challenges, including increased costs, inefficiencies, integration difficulties, alert fatigue, and an elevated risk of configuration errors. To address these issues, organizations must find a balance that ensures effective protection without overwhelming their resources and teams.
In this article, we will explore how organisations can establish a robust cybersecurity foundation while avoiding needless complexity.
How establish a strong foundation for protecting your business against cyber threats?
In today’s digital landscape, businesses face an increasing risk of cyber threats. To effectively protect against these risks, organizations must establish a strong foundation. While no security measure can guarantee complete protection, implementing the Critical Security Control based on CIS Controls framework, can significantly bolster your organization’s cybersecurity posture. According to research, organizations that implement the Top 7 Critical Security controls can reduce their risk of cyberattacks by over 85 percent. Implementing all 20 CIS Controls increases the risk reduction to around 94 percent (CISecurity.org). This percentage reduction in cybersecurity risk is based on the fact that these controls address common attack vectors and vulnerabilities that are frequently exploited by attackers. One effective strategy to significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks is by implementing the following Top 7 CIS Controls.
What is the purpose of CIS Controls?
Numerous frameworks have been developed to guide organizations in this mission, with the CIS Control, NIST, and ISO being some of the most recognized. However, there is a noticeable disparity between the CIS Control and these other frameworks, primarily stemming from their differing practicality and theoretical underpinnings.
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) Control is often celebrated for its pragmatic approach to cybersecurity. It provides a set of actionable and prioritized best practices that organizations can readily implement to enhance their security posture. These controls are based on real-world threats and vulnerabilities, making them practical and effective for organizations of all sizes. In essence, the CIS Control provides a clear roadmap for organizations to follow, allowing them to fortify their defenses against cyber threats systematically.
The framework is developed through industry consensus and continuously updated to address emerging threats. It is freely available, encouraging collaboration and knowledge sharing. Finding a balance between theory and practice is essential for effective cybersecurity. The CIS controls can be used alongside other frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, ISO 27001, or COBIT and provide measurable benchmarks for assessing cybersecurity maturity and facilitating audits.
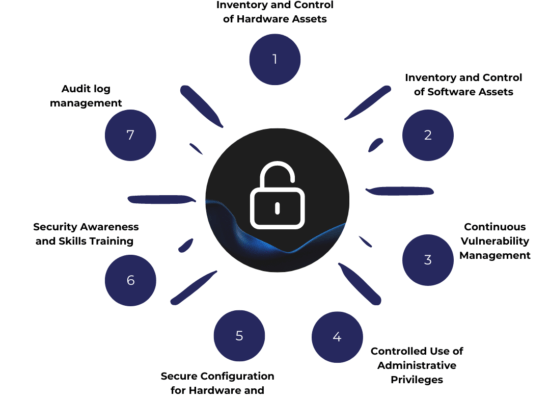
The Top 7 Critical Security Controls
The Top 7 CIS Control encompasses the six basic CIS Controls, to which we’ve added cybersecurity training, constituting the first line of human defense. Our customer experience leads us to firmly believe that cybersecurity deserves a decidedly operational approach that extends beyond the technological aspect and encompasses the human factor as well. The CIS Controls also provide a flexible framework for tailoring security measures to the needs of the organization based on its assets and available resources.
1. Inventory and Control of Hardware Assets
What is it?
Inventory and Control of Hardware Assets is a crucial security control that involves maintaining an up-to-date inventory of authorized hardware assets and implementing controls to monitor their use. This control ensures visibility and control over hardware devices, reducing the risk of unauthorized or unmanaged devices compromising security. Key aspects include :
- asset inventory,
- tracking,
- configuration management,
- access controls,
- patch management,
- and proper disposal procedures.
Why is it important?
Inventory and Control of Hardware Assets is crucial for cybersecurity as it provides visibility, access control, vulnerability management, incident response capabilities, compliance, and proper asset lifecycle management. Maintaining an accurate inventory helps organizations detect unauthorized devices, restrict access, address vulnerabilities, respond to incidents effectively, meet compliance requirements, and ensure a secure technology environment. Notable cyberattacks like Stuxnet, Shadow Brokers Leak, and Mirai Botnet emphasize the importance of proper hardware asset management in mitigating risks and protecting critical systems and data.
How do perform it?
Performing an Inventory and Control of Hardware Assets involves establishing policies, identifying authorized devices, implementing tracking mechanisms, configuring devices, enforcing access controls, managing patches and updates, properly disposing of assets, and conducting regular audits. The specific steps and tools may vary, and organizations should customize their approach based on their needs. Consulting with IT asset management specialists or cybersecurity professionals can provide valuable guidance.
Tools and procedures
The inventory and control of hardware assets encompass various tools and procedures essential for managing and securing hardware resources. These tools include IT Asset Management Software, Network Scanning Tools, Barcode or RFID Tagging Systems, and Configuration Management Tools, which assist in tracking and configuring devices.
Notable top tools for this purpose include ServiceNow IT Asset Management, Lansweeper, SolarWinds Network Configuration Manager, and Ivanti Asset Manager, offering features for comprehensive hardware asset management.
Open-source alternatives like Snipe-IT, GLPI, OCS Inventory NG, Ralph, and Open-AudIT provide cost-effective options. However, they may require customization to align with specific organizational needs, making a thorough evaluation necessary.
The associated procedures involve asset discovery, tracking, access control, patch management, disposal, auditing, and more, aiming to ensure compliance, security, and efficient hardware management.
2. Inventory and Control of Software Assets
What is it?
Inventory and Control of Software Assets refers to the process of identifying, tracking, and managing all software assets within an organization. It involves maintaining an accurate inventory of software licenses, versions, installations, and usage. This practice is crucial for effective software asset management, compliance with licensing agreements, and ensuring proper cybersecurity measures.
Why is it important?
Inventory and Control of Software Assets is crucial for cybersecurity due to several reasons. It helps ensure license compliance, manage vulnerabilities, prevent unauthorized software installations, facilitate effective patch management, and support incident response efforts. By maintaining an accurate inventory of software assets, organizations can mitigate legal and financial risks, protect against security vulnerabilities, and respond promptly to security incidents.
How do perform it?
Performing Inventory and Control of Software Assets involves several steps. These include discovering software assets, creating a comprehensive inventory, managing software licenses, monitoring software usage, managing patches and updates, and conducting regular audits and reporting. It is important to continuously update the inventory and implement effective processes and tools to ensure accuracy and compliance. Consulting with experts or utilizing software asset management tools can help streamline these efforts.
Tools and procedures
There are several tools available for Inventory and Control of Software Assets. Software Asset Management (SAM) tools like Flexera FlexNet Manager and Snow License Manager help track software installations, license compliance, usage, and vulnerabilities. Software discovery tools like Microsoft SCCM and Lansweeper help identify installed software on endpoints and servers. Vulnerability scanning tools like Nessus and Qualys scan software versions for known vulnerabilities. License management tools like Reprise License Manager and OpenLM assist in tracking and managing software licenses. These tools help organizations effectively manage their software assets.
Various tools are available for Inventory and Control of Software Assets. Software Asset Management (SAM) tools such as Flexera FlexNet Manager and Snow License Manager help track software installations, ensure license compliance, monitor usage, and identify vulnerabilities. Software discovery tools like Microsoft SCCM and Lansweeper help identify software installed on endpoints and servers. Vulnerability scanning tools like Nessus and Qualys scan software versions for known vulnerabilities. License management tools like Reprise License Manager and OpenLM assist in tracking and managing software licenses. These tools enable organizations to effectively manage their software assets.
3. Continuous Vulnerability Management
What is it?
Continuous Vulnerability Management is a cybersecurity practice that involves the ongoing identification, assessment, and mitigation of vulnerabilities within an organization’s IT infrastructure. It focuses on proactively managing vulnerabilities to reduce the risk of exploitation and potential security breaches.
Continuous Vulnerability Management encompasses various critical elements, including:
- vulnerability scanning,
- assessment,
- patch management,
- configuration management,
- remediation planning,
- monitoring, and reporting.
Why is it important?
Continuous Vulnerability Management is essential for maintaining a strong cybersecurity posture. It helps reduce risk by identifying and remedying vulnerabilities, taking a proactive approach to security. Compliance requirements can be met by implementing vulnerability management practices. Patch management is closely tied to vulnerability management, ensuring systems stay up to date with security patches. Asset management is improved through the continuous monitoring of vulnerabilities. By managing vulnerabilities, security incidents can be prevented, and remediation efforts can be prioritized based on severity. Continuous vulnerability management also allows for continuous improvement of security practices and the implementation of preventive measures.
4. Controlled Use of Administrative Privileges
What is it?
Controlled Use of Administrative Privileges is a critical security control that focuses on managing and restricting the use of administrative privileges within an organization. Administrative privileges provide users with elevated access and permissions that allow them to perform various administrative tasks, such as installing software, modifying system configurations, and accessing sensitive data.
Implementing controlled use of administrative privileges is crucial to mitigate the risks associated with unauthorized or misuse of these privileges.
Controlled Use of Administrative Privileges focuses on managing and restricting the use of administrative privileges within an organization. This involves implementing the principle of least privilege, managing privileged accounts effectively, enforcing separation of duties, applying access controls, monitoring usage, and properly managing privilege escalation. It is crucial to mitigate the risks associated with unauthorized or misuse of administrative privileges, enhance security, and ensure responsible usage.
Why is it important?
Controlled Use of Administrative Privileges is important for minimizing insider threats, mitigating the impact of compromised accounts, preventing unauthorized system modifications, and enhancing accountability and auditability. It helps reduce the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and system disruptions. Some famous attacks that exploit the misuse or abuse of administrative privileges include Pass-the-Hash Attacks, Golden Ticket Attacks, Lateral Movement Attacks, and Ransomware Attacks. Implementing controlled use of administrative privileges is crucial for maintaining a secure and trusted computing environment.
Tools and Procedures
Implementing controlled use of administrative privileges involves using tools such as :
- Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions,
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC),
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA),
- and procedures like privilege escalation and delegation policies, Access Control Lists (ACLs), regular account reviews and auditing, and privileged session monitoring.
These measures help manage and monitor privileged accounts, enforce access controls, prevent unauthorized access, detect suspicious activities, and ensure accountability. By implementing these tools and procedures, organizations can enhance the security of their privileged accounts and minimize the risk of unauthorized actions and data breaches.
It’s important to note that the specific tools and procedures used for controlled use of administrative privileges may vary depending on the organization’s infrastructure, size, and industry. Organizations should assess their unique requirements and consider consulting with cybersecurity professionals to determine the most suitable tools and procedures for their environment.
5. Secure Configuration for Hardware and Software
What is it?
Secure configuration for hardware and software involves implementing best practices and security measures to set up and configure devices and applications in a secure manner. This includes changing default credentials, disabling unnecessary services, enabling encryption, applying patches and updates, configuring access controls, and following secure coding practices. By doing so, organizations can minimize vulnerabilities and enhance the overall security of their systems.
Why is it important?
Secure configuration for hardware and software is crucial for mitigating vulnerabilities, implementing defense-in-depth, ensuring compliance, following the principle of least privilege, protecting data, managing patches, enabling effective incident response, and building trust and reputation. By implementing secure configurations, organizations can enhance their overall cybersecurity and reduce the risk of security breaches and data compromises.
Several notable examples of cyberattacks and instances of misuse of secure configuration for hardware and software include the WannaCry and NotPetya ransomware attacks, the Equifax and Target data breaches, and the Mirai botnet attack. These incidents emphasize the importance of promptly applying security patches, securing third-party access, implementing proper network segmentation, and securing and properly configuring IoT devices. Organizations must learn from these examples and prioritize secure configurations to mitigate vulnerabilities and protect against cyber threats.
Tools and Procedures
Securing configurations for hardware and software in cybersecurity involves using tools and procedures to minimize vulnerabilities and unauthorized access. Key tools include configuration management, vulnerability scanning, patch management, SIEM systems, asset management, and Group Policy. Procedures encompass defining secure baselines, implementing change management, conducting regular audits, controlling access, applying the principle of least privilege, encrypting data, and maintaining inventory and backups. Security awareness training, incident response planning, and documentation are also crucial. This holistic approach ensures a proactive stance in cybersecurity by minimizing risks associated with misconfigurations.
6. Security Awareness and Skills Training
What is it?
We live in an industry that is overwhelmed with technical buzzwords and jargon. That said, the reality is that tools don’t lead transformations, people do. Ask any security practitioner who has been around awhile and they will tell you just how critical the human factor is in cybersecurity and making security initiatives successful.
CIS Control 14 highlights the importance of security awareness and skills training for employees. It recognizes that employees can be a weak link in an organization’s cybersecurity defenses and emphasizes the need for ongoing training programs.
Key elements of CIS Control 14 include :
- implementing security awareness programs,
- conducting regular employee training sessions,
- communicating security policies effectively,
- promoting incident reporting and response,
- and continuously improving training programs based on feedback and emerging threats.
Security Awareness and Skills Training empowers employees to become active participants in defending against cyber threats and serves as a critical component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
Why is it important?
In summary, security awareness and skills training are essential for mitigating human-related cybersecurity risks, fostering a security-conscious culture, and ensuring compliance with regulations. By investing in training programs, organizations can empower their employees to become active defenders against cyber threats and contribute to a more robust cybersecurity posture.
How do you perform it?
There are several reputable security awareness and skills training programs available, including SANS Security Awareness, TryHackMe, Infosec IQ, KnowBe4, Inspired eLearning, and Security Mentor. These programs offer a range of training content, including modules, videos, quizzes, and simulated phishing exercises. They are designed to educate employees on various cybersecurity topics and improve their security awareness and skills. Organizations can choose the program that best suits their needs and customize the training content to align with their specific requirements. By investing in these training programs, organizations can enhance their employees’ ability to recognize and respond to security threats, ultimately strengthening their overall cybersecurity posture.
When selecting a security awareness and skills training program, organizations should consider factors such as content relevance and quality, delivery methods, customization options, reporting capabilities, and provider reputation. Best practices for developing effective security awareness include establishing a formal program, conducting a risk assessment, tailoring training content, communicating clear policies, conducting regular training sessions, implementing simulated phishing exercises, incorporating gamification, encouraging reporting and feedback, providing continuous education and reinforcement, and measuring and evaluating program effectiveness. By following these best practices, organizations can enhance security awareness and empower employees to protect against cyber threats.
Remember that security awareness is not a one-time event but a continuous effort. By implementing these best practices, organizations can foster a security-conscious culture and empower employees to become active participants in defending against cyber threats.
Tools and Procedures
Cybersecurity awareness and skills training tools can include online courses, interactive e-learning modules, security awareness campaigns, virtual labs and simulations, Capture the Flag challenges, cybersecurity games, and security awareness training platforms. The NICE Cybersecurity Workforce Framework provides a comprehensive taxonomy of cybersecurity tasks, knowledge, and skills required for various job roles within the field. The NICE Framework serves as a valuable resource for organizations and individuals seeking to identify and develop the necessary cybersecurity skills for their workforce.
7. Audit log management
What is it?
Audit log management, as outlined in CIS Control 6, involves the collection, secure storage, regular review, and protection of audit logs from critical systems. This practice helps organizations detect and respond to cybersecurity incidents, comply with regulations, and maintain a secure IT environment. Key elements include defining logging requirements, centralizing logs, setting up alerts, securing log data, regular backups, retention policies, and monitoring/logging component maintenance.
Why is it important?
Audit log management is essential for detecting and responding to incidents, ensuring compliance, establishing accountability, managing risks, and maintaining overall cybersecurity readiness.
Tools and Procedures
Audit log management involves both tools and procedures to effectively collect, store, review, and protect audit logs. Here are some key tools and procedures in audit log management:
Tools:
-
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: SIEM solutions like Splunk, LogRhythm, and IBM QRadar provide centralized log collection, correlation, analysis, and reporting. They offer real-time monitoring and alerting capabilities.
-
Log Management Platforms: Log management platforms such as ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), Graylog, and Sumo Logic help collect, store, and analyze logs for security and compliance purposes.
-
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions: EDR tools like Carbon Black and CrowdStrike collect endpoint logs and provide visibility into endpoint activities, aiding in threat detection and response.
-
Log Forwarders and Collectors: Tools like NXLog, Fluentd, and rsyslog collect and forward logs from various sources to centralized repositories or SIEM systems.
-
Log Analysis Tools: These tools, like Loggly, provide advanced log analysis capabilities to identify patterns, anomalies, and security incidents within logs.
-
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) Platforms: SOAR solutions like Palo Alto Networks Cortex XSOAR help automate responses to security incidents based on log data and alerts.
Procedures
Audit log management is vital for cybersecurity. It involves collecting, storing, reviewing, and protecting logs from critical systems. Tools include SIEM systems, log management platforms, EDR solutions, log forwarders, and log analysis tools. Procedures cover log collection, storage, review, alerting, correlation, investigation, compliance reporting, retention, access control, log rotation, testing, training, and documentation. This comprehensive approach helps organizations detect incidents, maintain compliance, and secure their IT environment effectively.
Master Your Critical Security Controls To Keep the Control of Your Cybersecurity
In the pursuit of effective cybersecurity, organizations must strike a balance between comprehensive protection and overcomplication. While no security control list is immune to criticism or weaknesses, the reality is that securing complex IT systems is challenging. Without core activities, practices and capabilities, it is nearly impossible. Organizations can gain a lot of ground by focusing on the absolutely critical fundamentals and executing them effectively at scale. By adopting the Top 7 CIS Controls, organizations can establish a solid cybersecurity foundation that effectively addresses their security needs while mitigating the risks associated with an overly complex security infrastructure.
If you have any further questions or need assistance in implementing the CIS controls or any other cybersecurity measures, do not hesitate to reach out. Together, we can strengthen your organization’s cybersecurity defenses and mitigate the risks associated with today’s ever-evolving threat landscape.

